Governance and compliance
European Cleaning Machines Recycling (ECMR) strives to continuously dismantle the products it receives in a manner that is respectful of the environment. ECMR also invests in the development of sustainable solutions and technologies for materials that can be easily dismantled and recycled for re-use in a way that minimises the environmental impact of the entire production process by generating new raw materials.
Transporting, loading and handling cleaning machines and equipment is optimised to the greatest possible extent and organised as sustainably as possible in order to reduce CO2 emissions. When machines and equipment are returned for treatment at the end of their useful life, ECMR guarantees sustainable processing through the use of appropriate equipment and methods that maximise the benefits of renewable energy sources and can be independently adapted to produce new products, thereby avoiding unnecessary waste dumping and incineration.
ECMR applies standardised procedures for dismantling, recycling and sorting the different parts in order to optimise the final result and maximise re-use of the products. It achieves optimum performance and minimises waste flows by separating and sorting the parts and components in preparation for recycling.

“WE DISASSEMBLE, RECYCLE AND UPCYCLE”
Based on expert assessment of the positive environmental impact of using parts and raw materials again in new product applications, we disassemble and recycle all the materials that can be re-used.
| – ABS parts | 100% recyclable/suitable for upcycling |
| – Aluminium parts | 100% recyclable |
| – Electric cables | 96% recyclable |
| – Electric components/motors | 69% recyclable |
| – Ferrous metals | 100% recyclable |
| – Galvanised metals | 100% recyclable |
| – Plastic/rubber | 84% recyclable / suitable for upcycling |
| – Polycarbonate | 100% recyclable / suitable for upcycling |
| – Polyethylene | 92% recyclable / suitable for upcycling |
| – Batteries | 100% recyclable / suitable for re-use |
COMPLIANCE
-
TRANSPORT
- Optimal use of load capacity for materials
- Transport rationalisation (combination shipments)
-
DISMANTLING, RECYCLING, UPCYCLING
- promote the re-use of recyclable materials
- develop sustainable technologies for improvement models and re-use
- component rationalisation
-
PRODUCTION
- ISO 14001:2004 certified production and process execution
- ISO 26000 certified, embedded in the CSR performance ladder
- simplify disassembly operations
- verify correct absorption and innovative areas of application for the re-use of materials
-
RE-USE
- identify the ideal dismantling procedures
- apply sustainable technologies for improvement models
-
DISPOSAL
- minimise discarded materials and disposal waste flow
- register relevant data and generate reports according to valid legislation and regulations
-
MACHINE INTAKE CERTIFICATION
- issue of certificates and statements regarding the history of (types of) machines and processing after intake
-
FACILITATION
- connect market partners and stakeholders in order to optimise and progress towards sustainable solutions that are designed to promote ecological benefits and circular business practices
1. LEGAL REFERENCES
In the next section, we inform you how each dismantled component of the machines and items of equipment is sorted for recycling based on its composition, in accordance with the relevant regulations and (European) directives that are in force in each individual country.
The following directives relate to recycling materials:
- Directive 2008/98/EC (Waste Framework Directive) of the Council of the European Community
- Directive 91/156/EEC of the Council of the European Community on non-hazardous waste
According to the above mentioned directives, waste must be used usefully in one of the following ways:
- Primary use as a fuel or other means to generate power
- Solvent reclamation/regeneration
- Recycling/reclamation of organic substances that are not defined as solvents
- Recycling/reclamation of metals and metal compounds
- Recycling/reclamation of other inorganic materials
- Regeneration of acids or bases
- Recovery of components used for pollution abatement
- Recovery of components from catalysts
- Oil re-refining or other re-uses of oil components
- Land treatment resulting in benefit for agriculture or ecological improvement
- Use of waste obtained from any of the operations numbered [R1] to [R10]
- [R12] Exchange of waste for submission to any of the operations numbered [R1] to [R11]
- [R13] Storage of waste pending any of the operations numbered [R1] to [R12] (including temporary storage, pending collection, on the site where the waste is produced)
CONTENTS
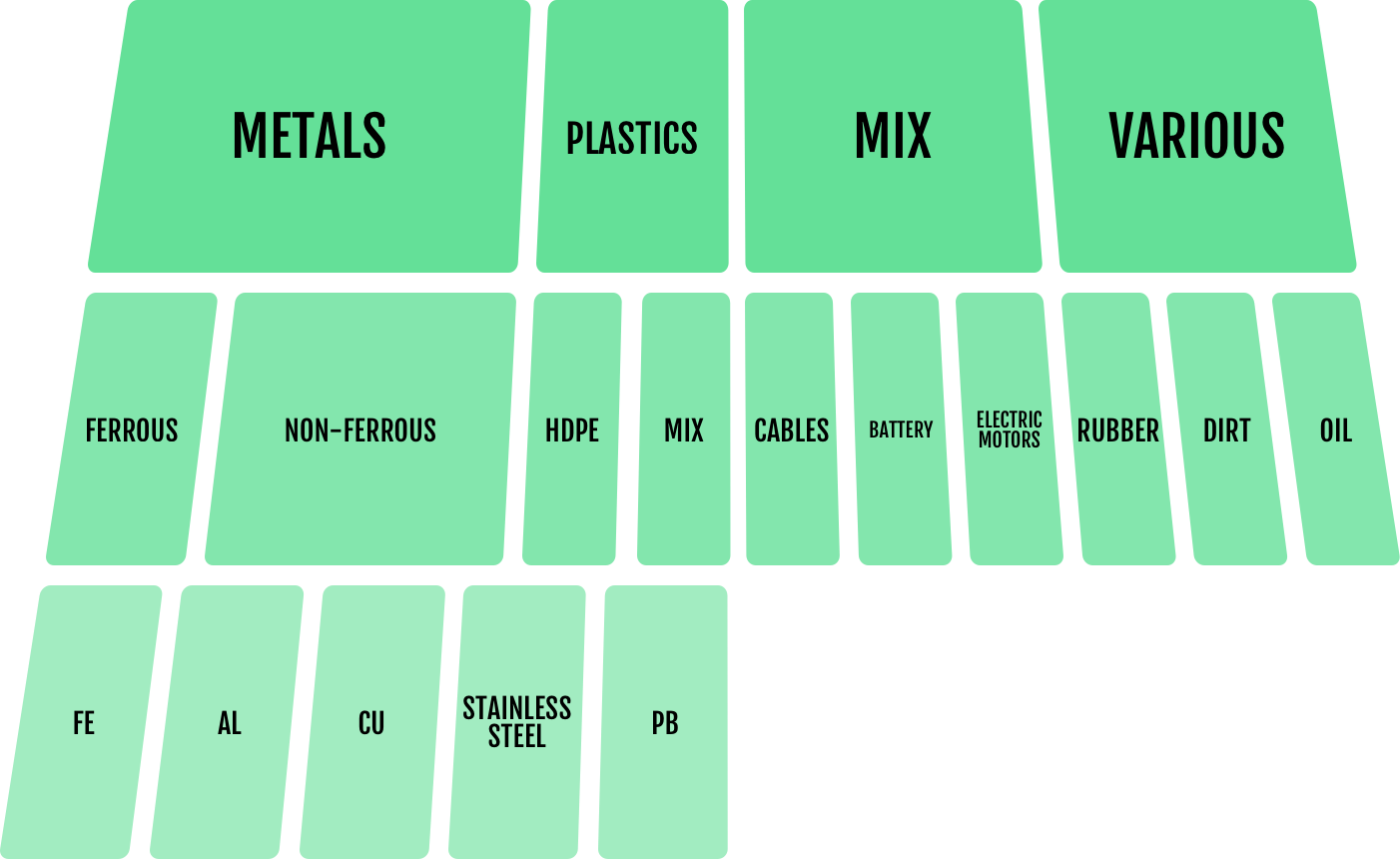
2.1 ABS components
2.2 Aluminium components
2.3 Electrical cables
2.4 Electrical components/motors
2.5 Ferrous metal parts
2.6 Galvanised metal parts
2.7 Plastic/rubber-based components
2.8 Polycarbonate components
2.9 Polyethylene components
2.10 Batteries
2. MATERIALS RECOVERED FOR RECYCLING, RE-USE AND UPCYCLING
2.1 ABS COMPONENTS
This category includes all components made in ABS for bodywork or protective covers.
For example: dispensers, vacuum cleaners, pressure washers and dashboards.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AS FOLLOWS:
- material identified and stored appropriately, processing and separation from any pollutants made from other materials [R13]
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- secondary raw material, generally in commercialised form
2.2 ALUMINIUM COMPONENTS
All parts of the machines made from aluminium and aluminium alloys are included in this category. For example: suction nozzle, suction nozzle systems and disc, machine steering columns.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AS FOLLOWS:
- material identified and stored appropriately, processing and separation from any pollutants [R13]
- direct reclamation for the metalworking industry [R4]
- storage for removal of foreign substances of a different composition [R13]
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- secondary raw material for the metalworking industry
- aluminium alloys, generally in commercialised form
2.3 ELECTRICAL CABLES
This category includes all cables used for wiring on the machines. They consist of copper conductors covered with heat-resistant plastic.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AS FOLLOWS:
- storage and processing to remove the plastic insulation. Grinding and granulation of the rubber, the metal scrap can be regenerated for use in the metalworking industry [R13]
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- direct reclamation for the metalworking industry [R4]
- plastic and rubber raw materials, generally in commercialised form
- copper and lead, generally in commercialised form
2.4. ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS/MOTORS
This category includes suction motors, brush motors, traction motors, drives and circuit boards.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AS FOLLOWS:
- material identified and stored appropriately, processing and separation from any pollutants [R13]
- disassembly to separate out components that are suitable for re-use (copper from the drives, metals from the element and plastics from the covers)
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- see the descriptions of the individual items of equipment for details of the specific materials
2.5 FERROUS METAL PARTS
All parts of the machines made from a metallic material, spray-painted in grey or black, are included in this category. For example: the frame, chassis and the suction nozzle support.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AS FOLLOWS:
- direct reclamation for the metalworking industry [R4]
- storage for removal of foreign substances of a different composition [R13]
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- ferrous metals or alloys, generally in commercialised form
- inorganic ferrous salts (acidic radical anions), generally in commercialised form
- secondary raw materials for the metalworking industry
2.6 GALVANISED METAL PARTS
This category includes all parts of the machines made from metals coated with zinc, nickel, both polished and unpolished. For example: levers, pulleys and shafts.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AS FOLLOWS:
- direct reclamation for the metalworking industry [R4]
- storage for removal of foreign substances of a different composition [R13]
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- ferrous metals or alloys, generally in commercialised form
- inorganic ferrous salts (acidic radical anions), generally in commercialised form
- secondary raw materials for the metalworking industry
2.7 PLASTIC/RUBBER-BASED COMPONENTS
Components made from rubber or derivatives thereof are included in this category. For example: handles, protective covers and motor casings.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AS FOLLOWS:
- reclamation for the rubber industry for adding to mixes [R3]
- reclamation for use in bitumen production [R3]
- storage for elimination of foreign substances of a different composition [R13]
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- rubber products, generally in commercialised form
- bitumen and mudguards, generally in commercialised form
2.8 POLYCARBONATE COMPONENTS
All parts made from polycarbonate are included in this category. For example: dispenser panels, windows, edge trims, light diffusers and lenses and dashboard fittings.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AS FOLLOWS:
- material identified and stored appropriately, processing and separation from any pollutants made from other materials [R13]
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- secondary raw material, generally in commercialised form
2.9 POLYETHYLENE COMPONENTS
All parts made from polyethylene are included in this category. For example: the fuel tanks, water tanks and bodywork for some machines and items of equipment.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AS FOLLOWS:
- material identified and stored appropriately, processing and separation from any pollutants made from other materials [R13]
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- secondary raw material, generally in commercialised form
2.10 BATTERIES
This category of machine parts includes hazardous chemicals.
THESE COMPONENTS ARE DISMANTLED AND SORTED FOR RECYCLING AND/OR RE-USE AS FOLLOWS:
- stored for re-use, remaining capacity > 50% (R1)
- complete component for re-use in ecosystems (R1)
- secondary fitment for re-use [R4] – [R7]
AVAILABLE FOR ECONOMIC RE-USE:
- direct reclamation for the power supply industry
- direct reclamation for the metalworking industry
3. CERTIFICATION
3.1 QUALITY AND THE ENVIRONMENT
ISO 14001:2015
This certificate guarantees that the company closely manages its environmental impact and continuously implements initiatives to reduce that impact.
3.2 POLICY AND STRUCTURE
ISO 26000
Review of the organisation with regard to performance in the area of society in which the company is active and the effects thereof on the environment. The certificate guarantees that general performance and the company’s entrepreneurial ability to continue to operate effectively are audited both internally and externally.
4. MEMBERSHIPS
4.1 CSR NETHERLANDS
CSR Netherlands (MVO Nederland) is the Centre of Excellence for Dutch and European companies that continuously strive to do business in a socially responsible manner. More than 2000 companies in the Netherlands are members of this networking organisation.
4.2 DUTCH WASTE MANAGEMENT ASSOCIATION
The platform for the full spectrum of representation at industrial, commercial, governmental and public level that is relevant to waste management. The association finances research and lobbies at high level in order to create a healthy and balanced business environment in the Netherlands and Europe, and to promote effective, practical and sustainable waste management.
4.3 ISSA (Worldwide Cleaning Industry Association)
A leading worldwide industry association that represents the interests of the cleaning industry and continuously professionalises the hygiene market in all its forms and facilitates long-term collaboration within this envelope.
4.4 NIWO NEDERLAND (National & International Road Transport Organisation)
The NIWO issues licences to the Dutch transport sector and aims to promote fair competition in the market for transporting goods by road, both domestically and in the cross-border segment.






